In a contest between the traditional landline and the cellphone the cellphone is winning nationwide. People in the US are ditching their landlines to save money and/or because those phones are becoming superfluous. By June of 2010 Texas had the third highest rate (32.5%) in the nation of households ditching their landline phones in favor of a mobile-only lifestyle. Texas also leads in the adoption of smart phones and mobile Internet access. In some metro areas of Texas, such as Dallas County, up to 62% of households can be reached only by calling a mobile phone.
The US Center for Disease Control (CDC) last week released its latest state by state breakdown on the "Wireless Substitution" trend. As of June, 2010 26.6% of US households were wireless only, meaning there was no landline in the house. In some states the numbers were higher than the average and some lower.

Rhode Island and New Jersey had the lowest rates of wireless substitution households at 12.8 percent, while Arkansas had the highest at 35.2 percent and Texas had the third highest household rate at 32.5 percent. The data suggest that economics are the primary driver of the decision to abandon the landline - lower income areas are going cell-only faster than more affluent areas.
CDC wireless surveys are also finding increasing percentages of so-called "cellphone-mostly" households. Cellphone-mostly households are households that do have a land line, but that line is used for FAX, security systems or other and it is rarely or never used to receive incoming calls. The January-June 2010 CDC survey found that 16% of households nationwide that do have a landline receive all or nearly all of their calls on a cellphone. This means that in order to reach 43 per cent of U.S. households as of June 2010, the only practical way to call their cellphone. If this additional statistic is added the number of cell-only households jumps dramatically in some states.
In Texas, 32.5% of all households are wireless only. But the "wireless mostly" number is 20.3% according to the CDC. Combine those numbers and almost 53% of Texas households rely primarily or exclusively on mobile phones. In several states the combined figure approaches or exceeds 50% of the population:Metro areas often have even higher cell-only adoption rates than the state as a whole. In Texas, 43.2% of households in Dallas County are wireless only. But the "wireless mostly" number is 17.7% according to the CDC. Combine those numbers and almost 61% of Dallas County households rely primarily or exclusively on mobile phones. The combined figure approaches or exceeds 50% of the population in most metro areas of Texas:
- Texas: 52.8%
- Arkansas: 50.9%
- Mississippi: 49.8%
- Arizona: 48.1%
- Nebraska: 47.3%
- Dallas County: Cell-Only (43.2%) + Cell-Mostly (17.7%) = 61.9%
- Bexar County: Cell-Only (29.1%) + Cell-Mostly (17.7%) = 46.8%
- El Paso County: Cell-Only (32.8%) + Cell-Mostly (14.8%) = 47.6%
- Harris County: Cell-Only (32.4%) + Cell-Mostly (22.1%) = 54.5%
The increasing prevalence of cell phone coverage in the U.S., and the consequent increase in the number of people who use their cell phone in place of a landline, makes it difficult to reach target populations by phone for pollsters, political organizations or political candidates.
As of December 2010, nearly a third (31%) of all mobile consumers in the United States owned smartphones, which are cellphones with app-based, web-enabled operating systems. A global study by research firm Gartner Inc. suggests that by as soon as 2013, mobile smartphone devices will overtake personal computers, including laptops as the most common way people access the Internet.
But nowhere in the U.S. is the shift from desktop and laptop computers to smartphones making as much of an impact as in Latino households or in African American and low-income households, in which the cell phone is often both the only household telephone and increasingly the device used to surf the Internet.
Smartphone total market penetration is highest among mobile users who are part of ethnic and racial minorities in the U.S. – namely Asian/Pacific Islanders (45%), Hispanics (45%) and African-Americans (33%), populations that also tend to skew younger. Meanwhile, only 27 percent of White mobile users reported owning a smartphone.
Although only 42 percent of Whites who purchased a mobile phone in the past six months chose a smartphone over a feature phone, 60 percent of Asians/Pacific Islanders, 56 percent of Hispanics, and 44 of African Americans who recently bought cellphones chose smartphones.
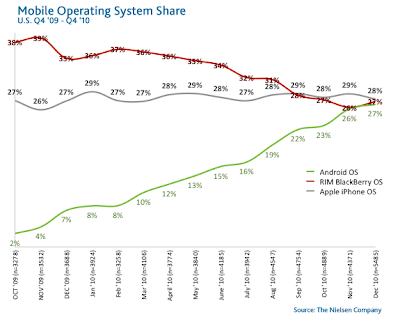
The competition between smartphone operating systems is a heated one. When it comes to the installed base, that is, U.S. mobile consumers who already own smartphones, it is a three-way tie between Blackberry RIM, the smartphone pioneer, Apple’s IOS, which revolutionized the smartphone and popularized mobile apps, and Android OS, the operating system created by Google which has been taking the market by storm.
Analyzing the preferences of those who purchased a smartphone in the past six months paints a different picture, however, one in which Android is clearly in the lead with 43 percent of recent acquirers purchasing an Android device, compared to 26 percent for Apple iOS and 20 percent for Blackberry RIM.
Apple’s iOs is the favorite among U.S. smartphone owners who are Asians/Pacific Islanders. Thirty-six percent of Asian/Pacific Islander who own smartphones have iPhones. On the other hand, RIM Blackberry is preferred by 31 percent of African-American smartphone owners.




No comments:
Post a Comment